
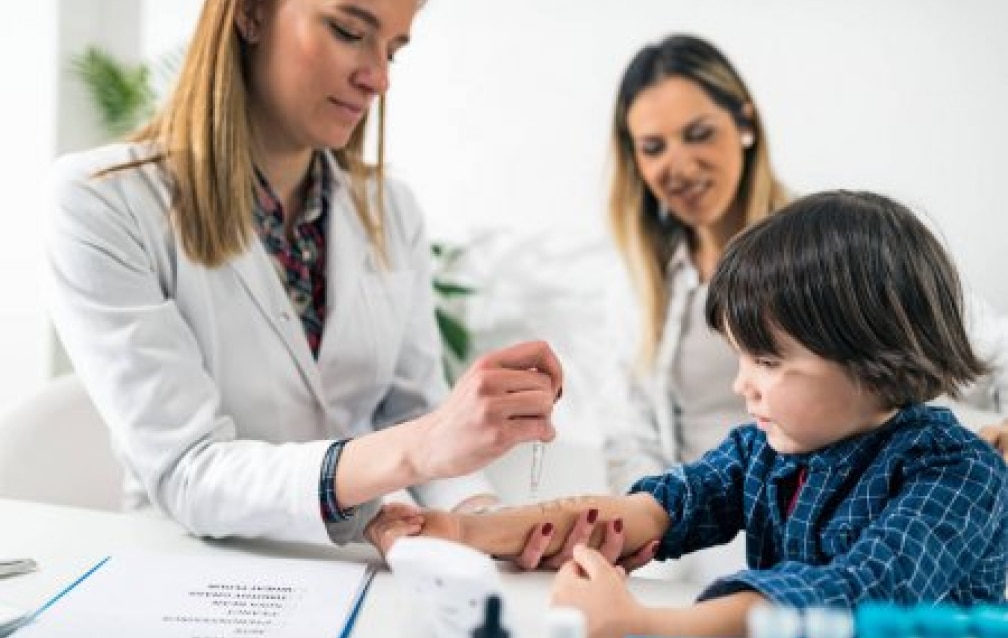
Allergy skin testing is the way that allergists look for the presence of allergies that can trigger various symptoms in the body. It is done by a prick method where a small amount of protein allergen is introduced under the skin to interact with allergen specific cells in the skin. The results show a small reaction (termed “wheal and flare”) when a patient has an IgE mediated allergy. Allergists use this test as the only rapid, sensitive, and painless method to determine the presence of allergies. The results are available to the patient in the office in fifteen minutes.
The following guidance is issued by the AAAAI (American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology)
When is Allergy Testing Appropriate?
Testing done by an allergist is generally safe and effective for adults and children of all ages. The allergen extracts or vaccines used in allergy tests performed by allergists meet U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requirements.
Symptoms
Symptoms which usually prompt an allergist to perform testing include:
Respiratory
itchy eyes, nose or throat; nasal congestion, runny nose, watery eyes, chest congestion, cough or wheezing
Abdominal
vomiting or cramping and diarrhea consistently after eating certain foods, eosinophilic disorders in the GI tract
insect stings
Severe reactions to stinging insect stings (other than swelling at the site of the sting)
Skin
itchiness, hives or eczema
Anaphylaxis
a serious allergic reaction that affects many parts of the body at the same time
The allergist may perform allergy skin testing to identify what allergic triggers may be behind your chronic or recurrent sinus problems.

When to Proceed with Caution
There are methods of allergy testing that the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) believes are not useful, effective or may lead to inappropriate diagnosis and treatment. These include: allergy screening tests done in supermarkets or drug stores, home testing, applied kinesiology (allergy testing by testing muscle strength or weakness), cytotoxicity testing for food allergy, Rinkel skin titration method, provocative neutralization testing, Immunoglobulin G (IgG) testing for food allergy or sublingual provocation.
Healthy Tips


Feel Better. Live Better.
An allergist / immunologist, often referred to as an allergist, is a pediatrician or internist with at least two additional years of specialized training in the diagnosis and treatment of allergies, asthma, immune deficiencies and other immunologic diseases. By visiting the office of an allergist, you can expect an accurate diagnosis, a treatment plan that works and educational information to help you manage your disease and feel better.
